FIXED STARS: Major Stars | 1000+ Stars | Constellations | About
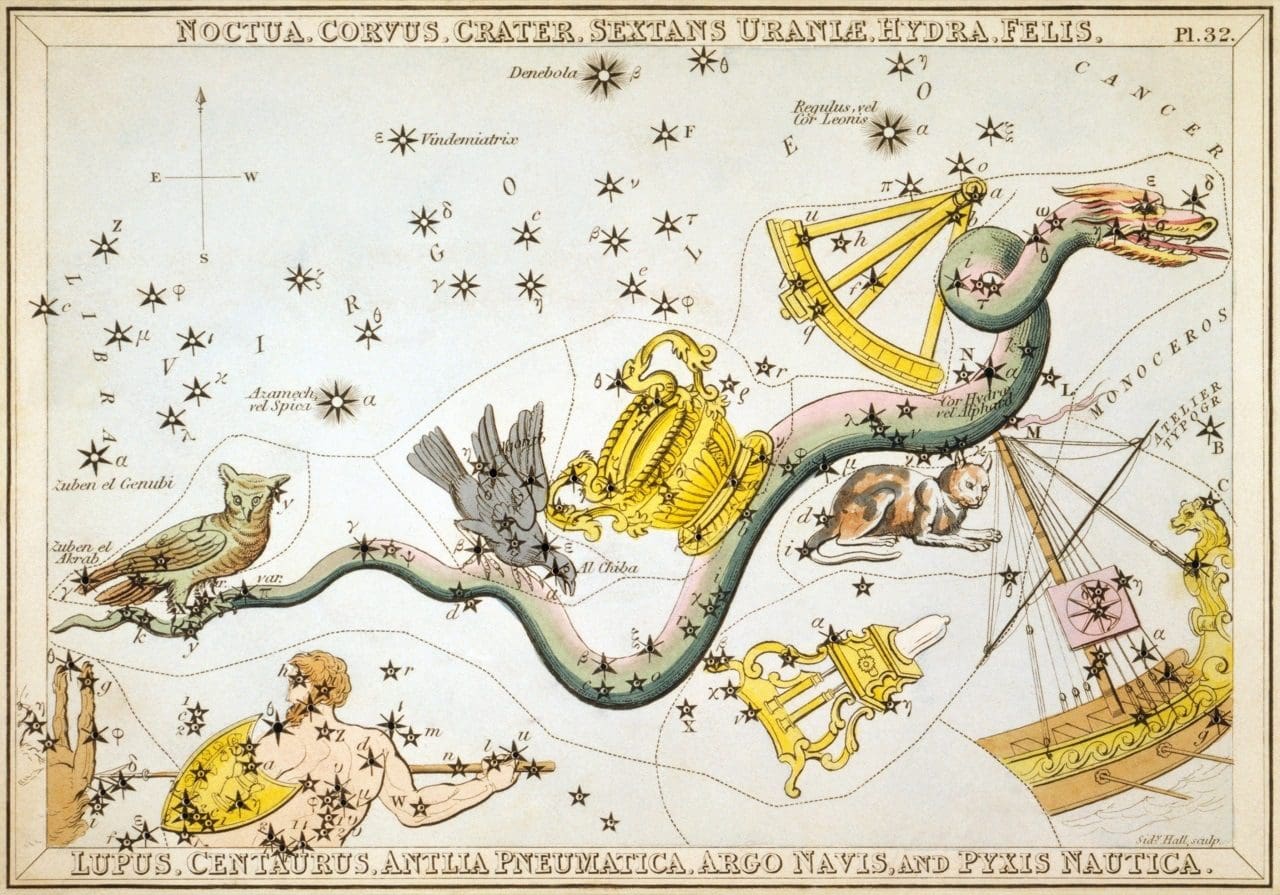
Constellation Antlia, the Air Pump, is a southern constellation bordering Hydra, Centaurus, Vela, Pyxis and the obsolete constellations Argo Navis and Felis.Antila was introduced by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in 1752 and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It spans 30 degrees of the zodiac in the Signs of Virgo and Libra.
Abbreviation: Ant
Genitive: Antliae
Antlia Constellation Stars
| 2000 | 2050 | Star | Name | Sp. Class | Mag. | Orb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 09♍26 | 10♍38 | θ Ant | A7 | 4.78 | 1°00′ | |
| 11♍00 | 11♍42 | ε Ant | K3 | 4.51 | 1°10′ | |
| 12♍27 | 13♍08 | α Ant | K4 | 4.28 | 1°20′ | |
| 03♎03 | 03♎45 | ι Ant | K0 | 4.60 | 1°00′ |
Antlia Astrology
Robson
ANTILIA PNEUMATICA. The Air Pump.
History. This constellation was added by de Lacaille in 1752 A.D., under the name Machine Pneumatica.
Influence. It is said to bestow prosperity, harmony and spiritual force. [1]
Allen
Antlia Pneumatica, the Air Pump, is La Caille’s Machine Pneumatique, at first Latinized as Machina Pneumatica; but astronomers know it as simple Antlia.
The constellation lies just south of Crater and Hydra, bordering on the Vela of Argo along the branches of the Milky Way; Gould assigning to it eighty-five naked-eye stars.
He thinks that α, the red lucida, may be a variable, as his observers had variously noted it as of from the 4th to the 5th magnitude, and Argelander entered both of these.
La Caille’s β lies within the present limits of Hydra. [2]
References
- Fixed Stars and Constellations in Astrology, Vivian E. Robson, 1923, p.28.
- Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning, Richard H. Allen, 1889, p.42-43.