FIXED STARS: Major Stars | 1000+ Stars | Constellations | About
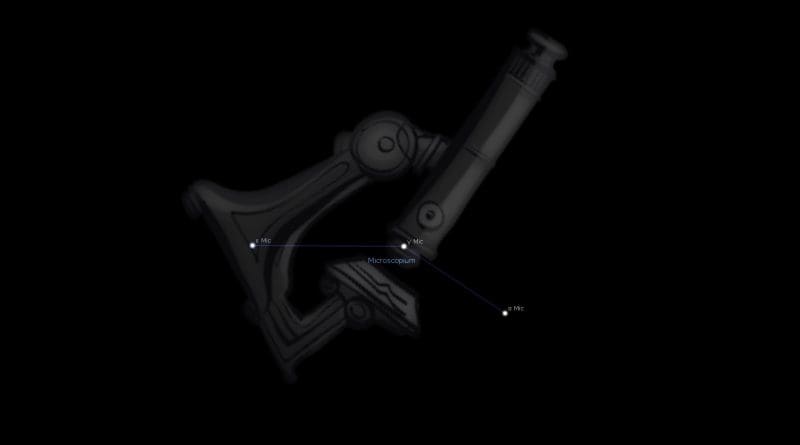
Constellation Microscopium The Microscope is a southern constellation bordering Capricornus, Sagittarius, Indus, Grus, Piscis Austrinus and the obsolete constellation Globus Aerostaticus.Microscopium was introduced by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in 1752 and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It spans 6 degrees of the zodiac in the Sign of Aquarius.
Abbreviation: Mic
Genitive: Microscopii
Microscopium Constellation Stars
| 2000 | 2050 | Star | Spectra | Mag | Orb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05♒37 | 06♒19 | α | G8 | 4.89 | 1°00′ |
| 08♒26 | 09♒08 | γ | G8 | 4.67 | 1°00′ |
| 09♒32 | 10♒14 | θ1 | A2 | 4.80 | 1°00′ |
| 11♒56 | 12♒38 | ε | A0 | 4.71 | 1°00′ |
Microscopium Astrology
Robson
MICROSCOPIUM. The Microscope.
History. Formed by de Lacaille, 1752.
Influence. It gives a careful, methodical, fastidious, meticulous and scientific nature. [1]
Allen
Microscopium, formed by La Caille south of Capricornus and west of Piscis Austrinus, although small and unimportant, contains sixty-nine stars, varying in magnitude from 4.8 to 7, the lucida being θ1. The constellation comes to the meridian in September, nearly due south of β Aquarii.
In its vicinity, perhaps including it, was an early figure referred to, in a German astronomical work of 1564 from Frankfurt, as Neper, the Auger, Ideler’s Bohrer, which he thus described:
It is situated at the tail of Sagittarius and Capricornus, and has many stars. At the head of the Neper two, and on the iron three. [2]
References
- Fixed Stars and Constellations in Astrology, Vivian E. Robson, 1923, p.51.
- Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning, Richard H. Allen, 1889, p.289.