FIXED STARS: Major Stars | 1000+ Stars | Constellations | About
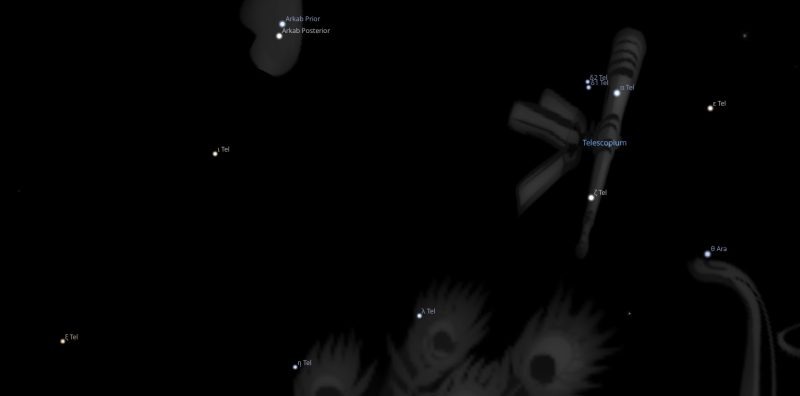
Constellation Telescopium The Telescope is a southern constellation bordering Ara, Corona Australis, Indus, Pavo and Sagittarius.Telescopium was introduced by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in 1752 and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It spans 21 degrees of the zodiac in the Signs of Sagittarius and Capricorn.
Abbreviation: Tel
Genitive: Telescopii
Telescopium Constellation Stars
| 2000 | 2050 | Star | Name | Sp. Class | Mag. | Orb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02♑06 | 02♑49 | ε Tel | G5 | 4.52 | 1°10′ | |
| 05♑04 | 05♑46 | α Tel | B3 | 3.49 | 1°40′ | |
| 05♑14 | 05♑56 | ζ Tel | G8 | 4.10 | 1°20′ | |
| 10♑06 | 10♑49 | λ Tel | A0 | 4.85 | 1°00′ | |
| 17♑28 | 18♑10 | ι Tel | G9 | 4.88 | 1°00′ |
Telescopium Astrology
Robson
TELESCOPIUM. The Telescope.
History. Formed by La Caille, 1752.
Influence. It is said to give a keen mind, prophetic abilities, and interest in philosophical, occult or historical subjects. [1]
Allen
Telescopium, or Tubus Astronomicus, was formed by La Caille between Ara and Sagittarius on the edge of the Milky Way, but in such irregular form that it encroached upon four of the old constellations; η Sagittarii having been taken as β to mark the Telescope’s stand; d Ophiuchi for its θ; σ was in Corona Australis; and γ was the υ of Scorpio. Bode had it in his Gestirne of 1805 as the Astronomische Fernrohr, crowding it in between Sagittarius and Scorpio; but Baily and Gould restricted it to the south of Scorpio, Sagittarius, and Corona Australis.
Gould assigned to it 87 naked-eye stars, the brightest a 3½‑magnitude.
Small as these are, two bore individual titles in Chinese astronomy; α being known as We, Danger; and γ as the mythological Chuen Shwo. [1]
References
- Fixed Stars and Constellations in Astrology, Vivian E. Robson, 1923, p.63
- Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning, Richard H. Allen, 1889, p.414.