FIXED STARS: Major Stars | 1000+ Stars | Constellations | About
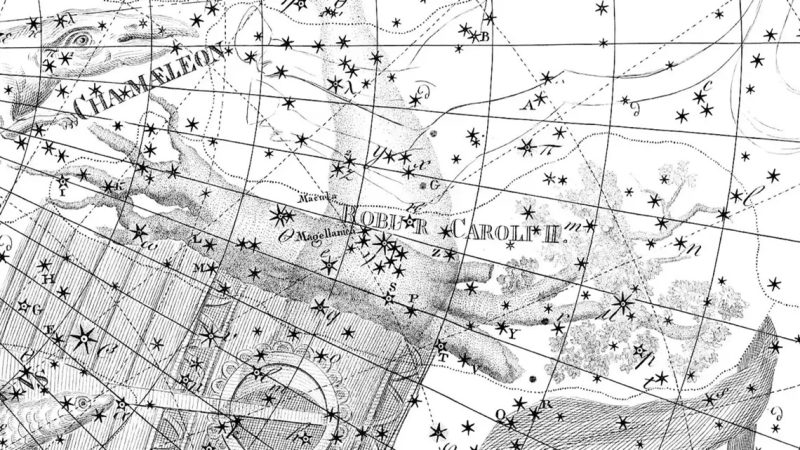
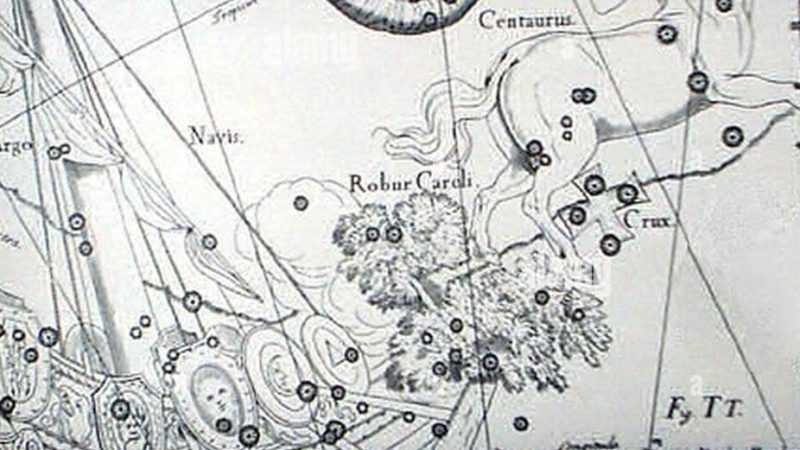
The obsolete constellation Robur Carolinum, Charles’s Oak, is a southern constellation bordering Carina, Vela, Centaurus, Musca, Chamaeleon and Volans.Robur Carolinum was introduced by Edmond Halley in 1679, and its stars now belong to Carina. It spans 33 degrees of the zodiac in the Signs of Libra and Scorpio
Abbreviation: Rob
Genitive: Roboris Caroli [1]
Robur Carolinum Constellation Stars
| 2000 | 2050 | Star | Name | Sp. Class | Mag. | Orb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16♎12 | 16♎53 | p Car | B4 | 3.30 | 1°00′ | |
| 17♎34 | 18♎16 | r Car | K3 | 4.45 | 1°30′ | |
| 17♎51 | 18♎32 | s Car | F2 | 3.81 | 1°00′ | |
| 20♎04 | 20♎49 | q Car | K3 | 3.39 | 1°00′ | |
| 22♎19 | 23♎01 | η Car | Foramen | p | 4.47 | 1°10′ |
| 22♎26 | 23♎08 | u Car | K0 | 3.78 | ||
| 22♎53 | 23♎35 | υ Car | Vathorz Prior | A9 | 2.92 | |
| 23♎11 | 23♎52 | w Car | K3 | 4.58 | ||
| 25♎07 | 25♎49 | x Car | G0 | 3.93 | ||
| 27♎03 | 27♎45 | y Car | A6 | 4.59 | ||
| 29♎11 | 29♎53 | θ Car | Vathorz Posterior | B0 | 2.74 | |
| 29♎27 | 00♏09 | z Car | G8 | 4.62 | ||
| 01♏58 | 02♏39 | β Car | Miaplacidus | A1 | 1.67 | |
| 04♏14 | 04♏55 | E Car | B2 | 4.67 | ||
| 07♏26 | 08♏07 | ω Car | Simiram | B8 | 3.29 | |
| 11♏19 | 12♏00 | G Car | F6 | 4.47 | ||
| 13♏23 | 14♏04 | K Car | A2 | 4.72 | ||
| 18♏05 | 18♏46 | I Car | F2 | 3.99 |
Robur Carolinum Astrology
Robson
ROBUR CAROLINUM. Charles’s Oak.
History. Formed by Halley, 1679, in commemoration of the oak in which Charles II lay hidden on 3rd September, 1651.
Influence. It is said to give a frank, honorable, generous, hospitable and steady nature. [2]
Allen
Robur Carolinum, Charles’ Oak, was formally published by Halley in 1679 in commemoration of the Royal Oak of his patron, Charles II, in which the king had lain hidden for twenty-four hours after his defeat by Cromwell in the battle of Worcester, on the 3d of September, 1651. This invention secured for Halley his master’s degree from Oxford, in 1678, by the king’s express command. But La Caille complained that the construction of the figure, from some of the finest stars in Ship, ruined that already incomplete constellation, “and the Oak ceases to flourish after half a century of possession,” although Bode sought to restore it, and Burritt incorporated it into his maps, assigning to it twenty-five stars. Halley’s 2d‑magnitude α Roboris was changed to β Argūs, now in Carina.
Reeve’s list of Chinese star-titles has only one entry under Robur —
Nan Chuen, the Southern Ship, θ, etc., but doubtful, incorrectly laid down. [3]
References
- SkyEye: Robur Carolinum
- Fixed Stars and Constellations in Astrology, Vivian E. Robson, 1923, p.59.
- Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning, Richard H. Allen, 1889, p.349.